- This Discussion Thread has 28 replies, 16 voices, and was last updated 1 week, 3 days ago by Adeyemi.
-
AuthorPosts
-
-
2024-04-12 at 4:22 pm #12378John-paulKeymaster
Thinking of your current or a past practice area provide an example of the train of transmission specific to that area. Fill in all ‘links’ in the chain with an example for each link:
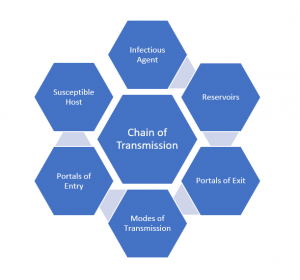
Infectious Agent:
Reservoirs:
Portals of Exit:
Modes of Transmission:
Portals of Entry:
Susceptible Host:
-
2025-12-26 at 1:17 pm #18077IbikemiMember
1. Infectious Agent
The germ that causes disease (bacteria, virus, fungus, or parasite). Eg, Influenza virus
2. Reservoirs
Where the germ normally lives and grows. Eg, Living organisms/Surfaces
3. Portals of Exit
How the germ leaves the reservoir. Eg, Coughing, sneezing, blood, saliva, feces, or skin wounds.
4. Modes of Transmission
How the germ spreads to another person. Eg, Direct contact, cough, sneezes, airborne, insects or contaminated objects
5. Portals of Entry
How the germ enters a new person. Eg, Nose, mouth, eyes or cuts in skin
6. Susceptible Host
A person who can get sick because their immune system isn’t strong enough to fight the germ. Eg, Ill Infants, elderly people and unvaccinated people-
2026-01-24 at 12:40 pm #18325AmandaMember
All staff and visitors can help reduce the spread of infectious agents. Ensuring staff are properly informed and trained on best practices and company policies. Employers need to make sure staff are trained and educated. They should provide an ample supply of easily accessible PPE for staff use and provide additional cleaning measures as needed to help break the chain of transmission. And always stress the importance of hand hygiene.
-
2026-02-19 at 5:25 pm #18548AdeyemiMember
Yes, I think all hands need to be on deck in the fight against the spread of infectious disease. Staff are being regularly trained in the various facilities where they work, family members and visitors can also be given adequate information by placing posters containing relevant information at strategic places such as the reception desks and notice boards in the facility.
-
-
-
2026-01-06 at 2:02 pm #18131DianeMember
Infectious Agent: CDIFF- Broad-spectrum antibiotics kill good gut bacteria, allowing C. diff to thrive.
Reservoirs: Surfaces, asymptomatic carrier, it is important that clients room should be cleaned paying attention to high touch surfaces, if available private room, one person use commodes, slings Hoyer lifts
Portals of Exit: mostly diarrhea
Modes of Transmission: when the person touches contaminated surface one
(eg would be when someone would touch their bedrail then their mouth (fecal-oral route).
Must ensure staff are to be using proper IPAC such as hand washing, gloves, proper disposal of equipment, ensuring proper signage to use PPE. do not share commodes, hand washing/ABHR.Portals of Entry: oral route mucous membranes
Susceptible Host: seniors or those who have been in hospitalized with use of Abx treatment immune compromised.
-
2026-01-28 at 9:23 pm #18378danaitMember
Thank you for providing C.diff as an example. Containment can be particularly challenging in environments with wandering residents. As a result, understanding and interrupting the chain of transmission is critical to preventing further spread.
-
-
2026-01-10 at 8:19 pm #18154Jessica-lynMember
Since its the season, and I work in long term care…
Infectious Agent: Influenza A
Reservoirs: Our residents, Their families, our staff and all others who come into our home!
Portals of Exit: Cough/Sputum.
Modes of Transmission: Droplet/Contact
Portals of Entry: Mouth, Mucous Membranes
Susceptible Host: Everyone, Though the elderly and younger population is more susceptible.
-
2026-01-18 at 7:16 pm #18219MunazzahMember
Isolation and appropriate use of personal protective equipment (PPE) play a critical role in preventing the transmission of Influenza A. As influenza continues to spread rapidly and undergo multiple mutations, it is essential to promptly report and document symptoms and take appropriate actions to protect public health.
-
2026-01-24 at 12:24 pm #18324AmandaMember
Influenza A has been the most common infectious agent in my LTC home this season. Some of the residents have been affected by both Covid-19 and Influenza A simultaneously. The infection rates increased over the holidays as many visitors were coming in to visit their family and friends. Its important to stress to visitors and staff to stay home if you are feeling unwell. Early detection of symptoms in residents and following proper precautions (isolation, PPE) all play a key role in reducing the transmission of infection.
-
-
2026-01-11 at 6:29 pm #18157AdeyemiMember
Infectious Agent: Covid-19 virus
Reservoirs: Surfaces such as tables, handrails, infected people
Portals of Exit: Coughing, Sneezing,
Modes of Transmission: contact with objects used or touched by an infected person, droplet
Portals of Entry: Mucous membranes in the nose, mouth, eyes
Susceptible Host: Advanced age, people with compromised or low level of immunity, people living with chronic diseases
-
2026-01-18 at 4:18 pm #18214RachelMember
One way to prevent the spread of Covid 19 and break the chain of transmission from either reservoir or portal of exit ( when infected pesron coughs) is to wear proper PPE for that resident that is in isolation. PPE Includes eye protection ( goggles), medical gown, N 59 mask and gloves, this way if you come into direct contact with that isolated resident or if they sneeze or cough while your there you, yourself are not coming into direct contact but the PPE is ensuring that the virus is not leaving the room, as properly doffing PPE and disposing of it keeps it contained.
-
2026-01-25 at 6:00 pm #18334MaameMember
Hello Rachel,
Thank you for sharing. I work in LTC and my unit was on COVID-19 outbreak, and you are right with wearing proper PPEs and the correct donning and doffing of PPEs is essential from preventing the spread. During shift exchange report my collegaue stated how you had to explain the importance of PPE use to a family member that came to visit their loved one that had COVID-19. I also wanted to add to your piece that education of use of PPEs is important for family members and visitors coming into the home. They might not know the seriousness of the virus and how quickly it spreads so education is extremely important.
-
2026-01-27 at 5:31 pm #18359DianeMember
Hello , I agree, ensure staff families those who enter rooms that are contaminated or on isolation should assured on how to don and doff PPE.
In one instance a family member told me he was a professional and didn’t need the education, I answered and Educated the importance for himself and his loved one he was visiting, pointed to signs placed outside of room along with cart full of mask face shields gowns N 95/surgical masks.
During the height of covid it was extremely important to educate all those outside our facility new ways to help us in breaking that chain of infection! We did well and was able to keep out numbers down.
-
-
-
2026-01-12 at 4:41 pm #18171SvetlanaMember
Infection Agent: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis(TB)
Reservoirs: Humans
Portals of exit: coughing, sneezing
Modes of Transmission: Airborne. Person to person through the air when someone with active TB speaks, sneezing, coughing
Portal of entry: Respiratory tract (Lungs) (via inhalation of Mycobacterium bacteria).
Susceptible Host: Very young children and Advanced age, people with compromised or low level of immunity, people living with chronic diseases, homeless people.-
2026-01-18 at 6:49 pm #18218MunazzahMember
Pulmonary Tuberculosis is a significant concern with many dying from the disease every year. Management of TB relies heavily on nursing care as nurses need to not just support patients but also educate them about potential transmission to reduce further spread.
-
2026-02-11 at 11:44 am #18497MargaretMember
You clearly outlined each link in the chain of transmission for TB and highlighted how easily it can spread through airborne particles. Identifying vulnerable populations such as immunocompromised individuals and those experiencing homelessness emphasizes the importance of early detection, isolation, and community health support.
-
-
2026-01-15 at 1:59 pm #18194KimberlyMember
Infectious Agent: Gastrointestinal Infection
Reservoirs: Animate and/or inanimate sources
Portal of Exit: Diarrhea, vomiting and saliva
Modes of Transmission: Pathogens on hands, surfaces, food, or water
Portal of Entry: Mucous membranes. Ex, touching your mouth after coming in contact with contaminated items or surfaces
Susceptible Hosts: Young children, elderly, anyone with a weakened immune system from illness or medications.-
2026-01-18 at 4:47 pm #18215RachelMember
One way to break the chain of infection is by following your work places policy for Managing Gastroinstinal infections, for example, if a resident is exhibiting signs and symptoms of it ie: having multiple loose stools is febrile and vomiting, that resident should be placed into isolation have isolation contact plus sign with the needed PPE and sanitizer as well as a waste bin for the PPE put into place and taking swabs (ex: PCR). This way you are protecting other residents by keeping them out of contact with the infected resident stopping the spread from resident to resident as well as ensuring staff are using the necessary PPE and apply hand hygiene when coming into contact with that resident for care to ensure that the Gastro infection is not leaving the room. This stops the spread from Resident to staff. When swabs are taken you are able to detect the virus or bacteria the resident has and properly treat according to what is identified.
-
-
2026-01-17 at 5:05 pm #18209RachelMember
Infectious agents: RSV
Resiviours : Tables, Beds, doorknobs etc..
Portal of exit: Mucus membranes, sneezing, coughing, talking,
Mode of transmission: Droplet, contact with person infected or contaminated item
Portal of entry: Mucus membranes located in eyes nose or mouth
susceptible host: someone who is immunocompromised, anyone who comes into contact with the infected person, children, elderly -
2026-01-18 at 6:00 pm #18217MunazzahMember
LTC
Infectious Agent: Shingles
Reservoirs: everyone who comes in contact with the virus
Portals of Exit: fluids from shingles rash/blisters, virus particles from the shingles blisters
Modes of Transmission: contact/airborne
Portals of Entry: respiratory system, skin contact
Susceptible Host: anyone among staff and residents with weakened immune system, visiting family with pregnant women or infant -
2026-01-22 at 10:19 am #18300KatrineMember
Visiting nurse:
Infectious agent: influenza virus
Reservoirs: an infected client of family member living in the home
Portals of exit: Respiratory secretions expelled through coughing, sneezing or talking
Modes of transmission: Droplet transmission through close contact, or indirect contact, via contaminated surfaces such as doorknobs, tablets, or shared medical equipment
Portals of entry: mucous membranes of the nose, mouth or eyes
Susceptible host: Elderly clients, individuals with chronic illnesses, immunocompromised clients, or unvaccinated household members.
-
2026-02-03 at 10:22 am #18433AlexandraMember
Hi Katrine,
As a visiting nurse I imagine it could be more difficult to interrupt the chain of infection when the family may not have good cleaning practices or lack understanding of all the ways infection can spread, also without having cleaning staff and other things that are present in facilities. I guess that teaching must be a large part of your practice as well as making sure that you follow all routine practices carefully to not spread things from one house to another.
-
-
2026-01-24 at 12:13 pm #18323AmandaMember
LTC Nurse
Infectious Agent: Blood- borne disease (HIV, Hepatitis)
Reservoirs: A resident living with blood borne pathogen
Portals of Exit: Blood, bodily fluids
Modes of Transmission: Contact with blood pathogen
Portals of Entry: Mucous membranes, broken skin, needle stick injury
Susceptible Host: Staff coming into contact with bodily fluids,
-
2026-01-25 at 5:46 pm #18333MaameMember
COVID-19 outbreak in LTC
1. Infectious agent: COVID-19
2. Reservoirs: Residents, staff, families and voulnteers.
3. Portal of Exit: respiratory tract of a coughing /sneezing resident
4. Modes of Transmission: Droplet/ Contact
5. Portals of Entry: Mucus membranes- mouth and nose.
6. Suspectible host: Immunocomprised indivduals.
-
2026-02-06 at 10:35 am #18460SheilaMember
Great example of the chain of transmission in an LTC COVID-19 outbreak. You clearly identified the infectious agent, reservoirs, and droplet/contact transmission, which are key in long-term care settings. Highlighting immunocompromised individuals as susceptible hosts is especially important, as this explains why outbreaks can spread rapidly and have severe outcomes in LTC residents.
-
-
2026-01-27 at 6:03 pm #18363IbikemiMember
Hello Amanda,
I agree with you on this important point you raised about how Infuenza A and COVID-19 can significantly impact LTC residents, especially during periods of increased visitation.
Encouraging staff and visitors to stay home when unwell, along with early symptom detection, isolation, and proper PPE use, is essential in reducing transmission and protecting vulnerable residents.
Though some families could be stubborn, where I worked the family took their mother on an outing while in Isolation, and the facility asked them to take their mother home for 5 days.
Adhering to instructions from some families could be challenging. -
2026-01-28 at 9:44 pm #18379danaitMember
Infectious agent: Noro virus ( a highly infectious agent that causes acute gastroenteritis)
Reservoirs:Found in symptomatic and asymptomatic individuals
Portals of Exit: virus exits the body through feces and vomit of infected individual
Modes of transmission: Noro virus is transmitted through fecal-oral route, contaminated surfaces or objects, contaminated food or water, and aerosolized particles produced during vomiting
Portals of entry: It enters the body through mouth, through contaminated water,hands and contaminated food
Susceptible host: Younger children, immunocompromised individuals, older adults living in hospitals or long term care facilities. -
2026-02-06 at 10:32 am #18459SheilaMember
Visiting Nurse
Infectious Agent: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Reservoirs: The client’s skin or open wound in the home care setting.
Portals of Exit: Wound drainage or contact with colonized skin during dressing changes.
Modes of Transmission: Direct contact via the visiting nurse’s hands, gloves, or contaminated equipment if proper hand hygiene or cleaning is not performed.
Portals of Entry: Breaks in the skin, surgical sites, or invasive devices of another client or the nurse.
Susceptible Host: Home care clients with chronic illness, poor skin integrity, weakened immunity, or advanced age. -
2026-02-11 at 11:41 am #18496MargaretMember
In the community setting, an example of the chain of transmission is influenza: the infectious agent is the influenza virus, the reservoir is an infected client at home, and the portal of exit is respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing. The mode of transmission can be direct contact or droplet spread, and the portal of entry is the mucous membranes of the nose, mouth, or eyes of another person. A susceptible host could be an elderly client with chronic conditions such as COPD or diabetes, who is at higher risk for complications.
-
-
AuthorPosts
- You must be logged in to reply to this Discussion Thread.